If you’re new to CAD and want to learn more about what it is, you have come to the right place.
Keep reading to learn what CAD is, who uses it, its benefits and drawbacks, popular CAD software, and what hardware your computer needs to efficiently create CAD models.
What Is CAD?
The term “Computer-aided design,” more commonly referred to as CAD, describes the use of computers to facilitate the design process across a variety of industries. Building a whole model in an imagined digital environment is achievable using CAD software, allowing you to see characteristics like height, width, distance, material, or color before the model is used or manufactured for a specific application.
The first computer graphic application, called “SketchPad,” was developed by computer scientist Ivan Sutherland in 1963. It allowed users to write or draw basic shapes directly on a screen with the aid of a special pencil.
Initially, CAD was mainly used for research, but in the 1970s, major aerospace and automotive corporations began creating their own software, thereby increasing its use in other industries in the 1980s. It wasn’t until the 1990s that programs like AutoCAD and CATIA were developed, enabling CAD usage across numerous professional fields.
Who Uses CAD?
A wide range of occupations employ computer-aided design in their workflows. CAD software is extensively used for projects in the arts, engineering, and architecture fields. The following are just a few of the many industries that use CAD.
Mechanical Engineering
In the field of mechanical engineering, CAD software, such as AutoCAD or SolidWorks, helps with designing models so that they can be more easily understood without the need to create a physical prototype. In addition, the models can then be easily materialized as physical prototypes with machines like a CNC or a 3D printer.
Architecture / Construction
Today’s architects design 2D models in CAD programs like AutoCAD, so that customers can quickly understand sizes and layouts when designing a building or house.
Instead of the traditional method of drawing out mock-ups by hand, with CAD software, you can dramatically increase your productivity and easily make changes to the file without having to start over from scratch.
Fashion Industry
Designers in the fashion industry often use CAD software, such as when creating a three-dimensional model of a ring.
In addition, programs like AutoCAD make it possible to quickly draw up 2D layouts for individual parts that come together to create a completed product. One example would be designing all the components needed to make a leather handbag, which can be easily laid out with CAD.
Electrical Engineering
CAD software is used extensively by electrical engineers for designing electrical circuits and printed circuit boards (PCBs). It can also help electrical engineers lay out electrical systems for buildings and machinery.
Sign up for AutoCAD Online Training Course
CAD Benefits
Using CAD software can provide engineers and designers with a number of benefits over traditional technical drawings and manual drafting, including:
- Lowering design production costs.
- Completing projects faster, due to efficient design and workflow techniques.
- Making modifications without affecting other design components or negating the need to completely rework a sketch.
- Creating higher-quality designs with built-in documentation (such as angles, dimensions, and presets).
- Designing models that are more precise, easier for collaborators to read, and more detailed than hand-drawn drawings.
- Utilizing digital files to simplify communication with coworkers and clients.
CAD Drawbacks
It can be difficult to pinpoint CAD’s drawbacks because it has become so integrated in production workflows across a variety of industries. But there are some potential drawbacks.
- It can take a lot of time and money to develop digital 3D models, depending on the detail required.
- CAD proficiency can take a long time to master and can be expensive to learn.
- Staying up to date on the latest CAD software upgrades can be costly.
2D CAD Drafting vs. 3D CAD Modeling
While CAD has become synonymous with 3D modeling, that doesn’t mean that 2D CAD doesn’t have practical applications.
2D CAD Drafting
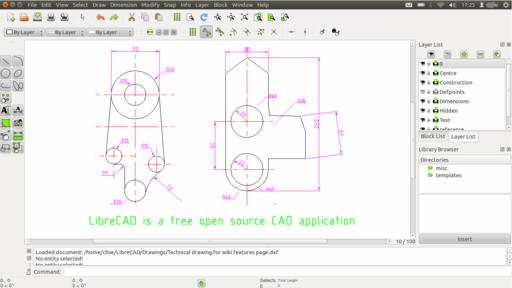
Most of us are familiar with two-dimensional computer-aided design, or 2D CAD. These models are two-dimensional, flat drawings that display the shapes, layouts, and specifics needed to reproduce or construct the item being designed. A variety of industries utilize 2D CAD drawings, including fashion, interior design, civil engineering, architecture, the automotive industry, cartography, and aerospace.
There is definitely a demand for CAD designers who have the skills and ability to digitally conceptualize an idea in two dimensions.
3D CAD Modeling
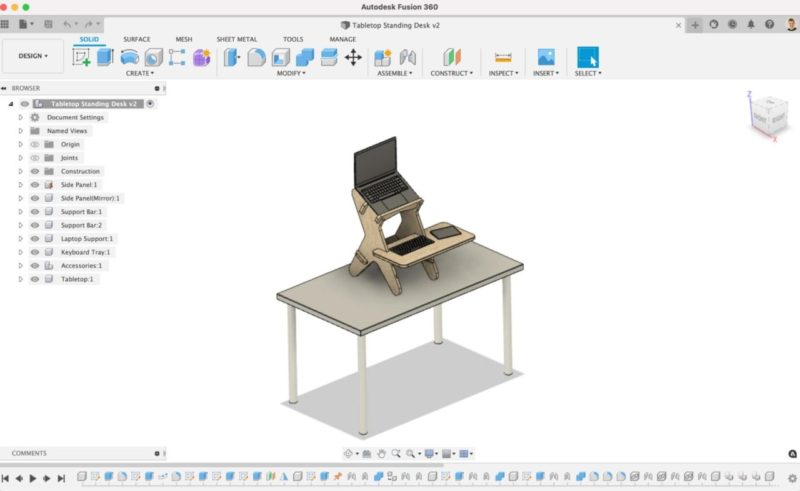
Three-dimensional computer-aided design is known as 3D CAD. It can often be used in ways that are comparable to 2D CAD drafting. So how are they different?
With 3D CAD, a greater amount of detail can be incorporated into the models, which can better simulate real-world applications as well as the assembly and interaction of multiple components.
To put it another way, both 2D and 3D CAD can show the size and shape of an object, such as the contours and dimensions of a new car model or the floor plans of a building. But with 3D CAD, you can also test the model’s functionality and better communicate all the necessary information for production.
Popular CAD Software
There are a number of paid and free CAD software that are readily available for designers, engineers, and home enthusiasts. Some CAD software are developed for the manufacturing, engineering, and architecture industries, so it’s important to not only look at how much the software costs but what its capabilities are and how well the software meets your needs.
For example, at the time of this article’s publication, AutoCAD and SolidWorks cost around $1,900 and $2,800 per year, respectively. Both are over-powered for most hobbyists and non-professionals, so investing the money in professional-level software is probably not the best use of a limited budget when there are many other CAD software options available that provide beginner- and intermediate-level tools and functions at a fraction of the price.
With that being said, here four of the more popular industrial software worth looking at if you are planning to work in a field that requires CAD skills.
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is the most widely used application in CAD today, with powerful functions and tool sets that can help you quickly create 2D vector drawings and 3D surfaces. Additionally, AutoCAD data can be easily saved and maintained using its cloud service, enabling 24/7 access to your files wherever you may be.
Sign up for AutoCAD Online Training Course
SketchUp
SketchUp is often used by professionals who are just getting started with CAD. The software’s interface is quite straightforward and easy to use. However, because the interface is quite simple, many features that more comprehensive competitors offer are absent from this software. Unless you are completely new to CAD design, you should consider your production needs before choosing SketchUp.
MicroStation
MicroStation (offered by Bentley Systems) is CAD software that is designed to handle high volumes of data required by infrastructure projects. The software has a powerful environment that allows the construction and management of graphical objects representing map elements. Maps that are considered difficult to create in some other software (such as AutoCAD) are easily made in MicroStation.
SolidWorks
SolidWorks is a powerful 3D CAD software that integrates a variety of supporting tools. At the same time, the software is widely applied in fields from construction and architecture, to interior designing and more.
Since its initial release in 1995, SolidWorks has made many outstanding strides in features and performance, while always meeting the expectations of 3D CAD professionals in the engineering and industrial sectors.
Other Popular CAD Software Worth Checking Out
In addition to the four CAD software listed above, there are many other useful options.
- CorelCAD is designed as a cost-effective alternative for businesses and professionals.
- IronCAD is design to run faster than any other CAD system to produce design iterations, proposals, and production drawings.
- CADTalk is a CAD integration solution that automates the laborious entry of data into ERP systems from CAD applications.
- Onshape is the first and only product development platform to offer professional-grade CAD capabilities with integrated data management in order to fuel more cost-effective and agile design processes.
- LibreCAD is a free Open Source CAD application available for Linux, Windows, and Mac. Free help and documentation are provided by a sizable and passionate user, contributor, and developer community.
- Solid Edge is inexpensive, easy to use, and covers every aspect of the product development process. The software combines the versatility and control of parametric design with the effectiveness and simplicity of direct modeling, all with the help of synchronous technology.
- Altium Designer gives engineers access to a single view of all facets of the PCB design process with its unified design environment, including the schematic, PCB layout, and design documentation. Engineers can swiftly produce high-quality products by having access to all of their design tools in one convenient location and completing the whole design process within the same user-friendly environment.
- CATIA is a multi-platform software package created by Dassault Systèmes for CAD, manufacturing, engineering, 3D modeling, and product lifecycle management.
Hardware Configuration Tips for Running CAD Software
Workstations that are used for CAD design are different from the usual home and office computers, requiring greater demands and more powerful specs. To know what you need for your computer, it’s best to refer to the software’s official specification requirements page.
Processor (CPU)
Unlike gaming computers, for CAD graphics you do not need to choose a chip with many cores. It is important to note that the higher the clock speed, the better, because it will not only help your CAD software render faster and more smoothly, but also have an impact on the software’s performance.
Recommended Processor Speeds
- AutoCAD:0+ GHz processor
- SketchUp:0+ GHz processor
- MicroStation:0+ GHz processor
- SolidWorks: Not provided (several third-party sites have tested this and recommend anywhere between 3.0–3.5 GHz processor)
RAM
The RAM determines how fast or slow the system’s processing power is. CAD software is said to be a “RAM killer” because it consumes a lot of the machine’s RAM when processing tasks.
Although RAM is only temporary storage, when the RAM memory is full, it affects the data transfer to the cache. If you use RAM with a higher bus speed, the software should run faster and smoother. (This is a generalization on the bus speed’s effect on performance, so we suggest researching this topic in greater detail before purchasing RAM that is specific to your computer’s specs.)
AutoCAD, SketchUp, and SolidWorks recommend at least 8GB RAM, while MicroStation recommends at least 16GB RAM.
Graphics Card
When it comes to CAD, the graphics card is likened to the heart of the PC. It has the important task of handling the color related work of the image displayed on the screen.
While most high-end GPUs can probably handle any of the CAD software included above, it’s best to double-check with the vendor, since several of them have a list of certified graphics cards that have been tested and proven to function correctly with the software.
To help you quickly find this information, we have provided links to the relevant page on each software’s official website below.
Official Graphics Card Recommendations
Hard Drive
SSDs are significantly faster than HDDs in reading and writing data. Therefore, to optimize your storage space, it is recommended that you use a combination of the two hard drive types, with a 256GB SSD for the primary disk and a 1TB HDD (or larger) for storing files locally. This has the effect of speeding up boot time and accessing data, as well as opening up large files and retrieving data more quickly, reducing latency so that the machine works faster, and simply providing an overall better working experience.
It’s also possible that your CAD software of choice will offer the ability to store and edit files on the cloud, which is worth considering as an option instead of using a large HDD.
If you want to try CAD, we recommend the free trial version
If you want to try using CAD, we recommend the free trial version.
CAD software may seem difficult, but anyone can use it once they learn it.